The Trend Monitor has a strong history of providing early insights into emerging social, technological, economic, environmental, and political (STEEP) trends, and their strategic consequences, for the aviation industry. As a pioneering organization, for this year’s trend report, we will adopt a new AI agent-powered approach to develop scenarios for aviation in the year 2035.
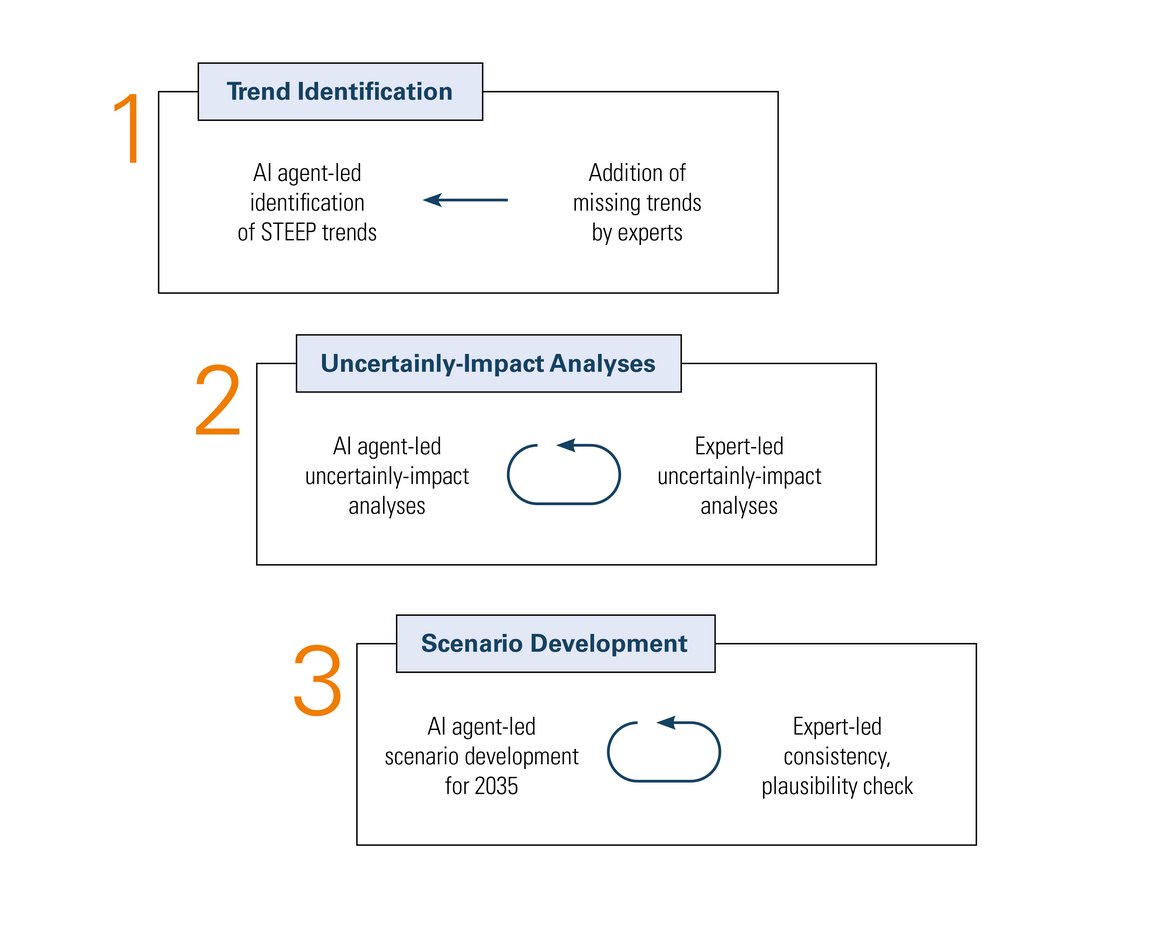
The scenario approach has three steps:
- Identification of STEEP trends for global aviation,
- An uncertainty-impact analysis of the trends,
- The development of 2035 scenarios based on critical trends.
In each step, inputs from experts are combined with the outputs of proprietary AI agents.
AI agents are artificial entities founded on a Large Language Model (LLM), such as ChatGPT. LLM-based agents are capable of autonomous decision-making and creativity, task decomposition, adapting to circumstances and errors, as well as interacting with other agents and tools.
For the purpose of this project, AI agents can be understood as specialized instances of LLMs. The new Trend Monitor utilizes various multi-agent systems, in which each agent serves a very specific purpose, performs a very specific task.
AI agents discover STEEP trends that can shape the next decade for global aviation. Each trend is accompanied by a fact-based description of current observations and available projections, and a citation of the sources that inform the descriptions. These trends are then shared with experts, who are asked to identify trends that the agents may have missed.
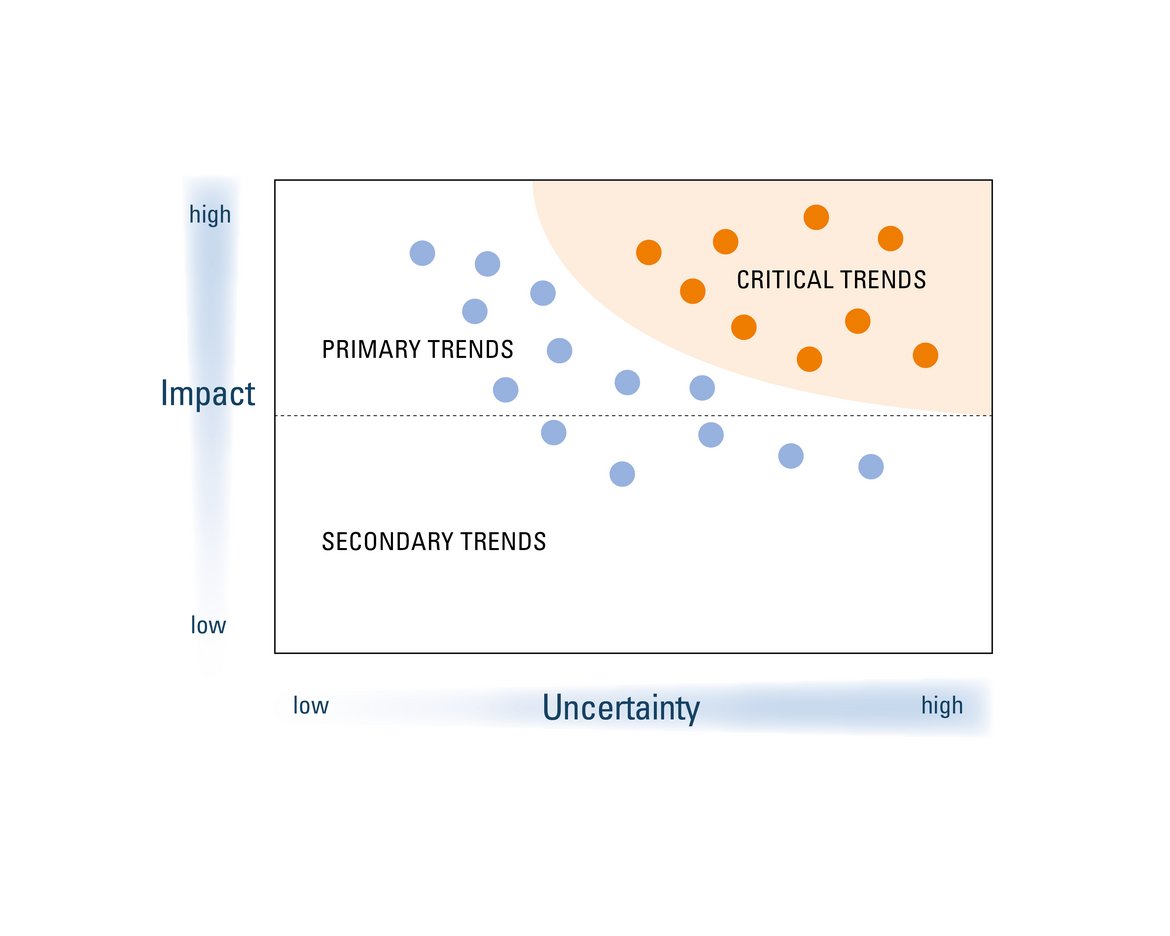
In addition to suggesting trends, experts are requested to score the trends on uncertainty and impact. The objective of the uncertainty-impact analysis is to evaluate potential risks or opportunities by examining:
- the level of uncertainty surrounding a trend (regarding its level of development by 2035, its pace of occurrence etc.)
- the potential impacts on different aspects (such as business models, revenue streams, passenger behaviors etc.) and stakeholders, whenever the trend fully develops.
In parallel to the expert-scoring, trends will also be scored by AI agents. These scoring agents are still being created, but early results demonstrate promise and certain advantages.
By combining both sets of scores, “critical trends”, i.e. highly impactful and highly uncertain trends, are identified.
Once the set of critical trends has been obtained, the two most impactful trends with high uncertainty are chosen to develop future scenarios with. It will be ensured that the two trends do not belong to the same STEEP trend type and that they are highly independent of each other. By varying the states of these two trends, a scenario matrix depicting four strategic scenarios for 2035 is created.
These four scenarios will then be described through a combination of AI agent-led scenario development and expert-validation. To describe the scenarios, some of the other critical trends may be used, in a manner that the scenarios are consistent and plausible. Eventually, agents are used to recommend how stakeholders should strategize, prioritize and prepare for these scenarios.
Our AI agent-powered approach offers significant advantages. In comparison to manual process.
- AI agents enhance time- and cost-efficiency: Agents process efficiently and rapidly, vast amounts of data from a wide range of sources, at nominal cost.
- AI agents enhance scalability: Agents can scale to executing several different tasks (e.g. research to brainstorming to creative writing), to include several sources, and to examine multiple trend-types.
More importantly, employing multi-agent systems, rather than generalized LLMs has enabled
- Higher quality through control: The agents provide factual, reliable responses. Through a combination of parameter-tuning and well-defined prompts, the agents are forced to focus only on certain manageable tasks, which prevents them from generating hallucinations, assumptions, or baseless predictions.
- Profoundness: Agents' collaborative truth-seeking results in profound results. A complex project like STEEP analysis has been broken down into sub-tasks, which are then assigned to a group of several agents. These agents focus on their tasks autonomously, but subsequently collaborate within the multi-agent system. This leads to detail-rich outputs that are not possible to obtain with generalized LLMs.
- Relevancy: The agents’ responses are relevant. Most LLMs only have access to information up until some date in the past. These agents, however, are able to access to the most up-to-date information.
These agents are developed through agile software development. This means different agentic-workflow systems, prompts, and large language models are rapidly iterated through, to identify the combinations that give the best possible results.
At this point, it should be noted that our agents are the worst they ever will be. As LLMs get smarter, as the scoring agents and scenario agents are developed, as further iterations are executed, Bauhaus Luftfahrt will be in a position to build agents that better identify and describe trends, better score them, and better develop scenarios (at a cheaper and faster rate).
References
- Schneider, A. (2024, April 04). Aviation’s metaverse future in four scenarios. TNMT
- Wulf, T., Meißner, P., & Stubner, S. (2010). A scenario-based approach to strategic planning: Integrating planning and process perspective of strategy. Leipzig, Germany: HHL Leipzig Graduate School of Management.
- Xi, Z., Chen, W., Guo, X., He, W., Ding, Y., Hong, B., ... & Gui, T. (2025). The rise and potential of large language model based agents: A survey. Science China Information Sciences, 68(2), 121101.